主な違い – 原油とシェールオイル
シェールオイル
Fossil fuels are non-renewable energy sources which are formed by sedimentation of plant and animals that died hundreds of millions of years ago. These fuels can be subdivided into two categories as petroleum and non-petroleum energy sources. Petroleum is the most abundantly used source of energy, and it generally exists in the liquid state. Crude oil is an example of petroleum, which consists of mixtures of hydrocarbons and variable amounts of sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen containing compounds. In contrast to crude oil, Shale oil is a non-petroleum fuel, which naturally exist in a solid state as an oil shale rock or kerogen. This organic sediment should be thermally decomposed to obtain liquid shale oil. Therefore, shale oil is also called as a synthetic crude oil. The main difference between crude oil and shale oil is that crude oil naturally exists in a liquid state whereas shale oil naturally exists in a solid state.The Figure 1. illustrates the classification of the earth’s organic sediments according to its physical state, hydrocarbon occurrence, and production.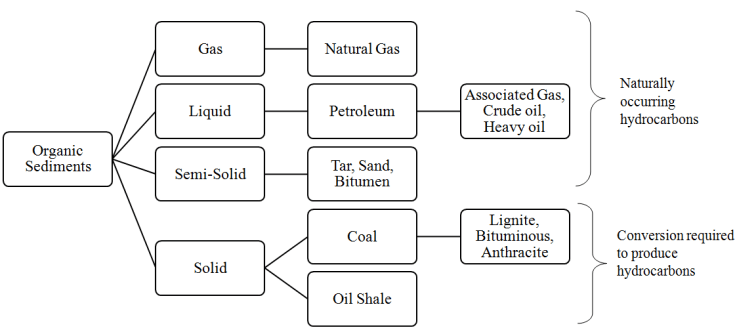
原油とは
原油は、炭化水素とヘテロ原子化合物の濃い色の高粘度の複雑な混合物で、蒸留によって分留することができる。
原油は、貯留層に存在する天然の燃料の状態を示している。
そのため、最終用途の要求仕様を満たすために精製される必要がある。
ガソリン、ディーゼル、航空燃料などの輸送用燃料のほとんどは、原油の分留物です。
これは精製油と比較して経済的価値が低い。
原油の化学組成や色、臭い、揮発性、比重、粘度などの物性は、原油の原産地の圧力、体積、温度によって変化する。
下表は、原油の代表的な蒸留の留分を示したものです。
| — | — | — |
| 沸点範囲/℃|炭素原子数|炭素製品|<30>|C1-C4| C1-C4|天然ガス、メタン。
Table 1. Fractions of typical distillation of crude oil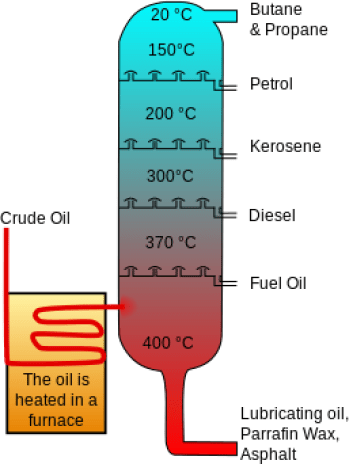
さらに、原油は硫黄分の含有量によって2種類に分けられる。
硫黄分が0.5%(w/w)より多いものをサワー原油、0.5%(w/w)より少ないものをスイート原油と呼ぶ。
この低硫黄原油は、エンジンの腐食を抑え、燃料燃焼時のSOxの発生量も少ないため、環境に優しい原油です。
シェールオイルとは?
シェールオイルは、オイルシェールと呼ばれる特殊な瀝青質の岩石の中に固体として自然に存在する非従来型の燃料です。
このオイルシェールは、有機物を多く含む珪藻土の堆積物で、熱分解によりシェールオイルと呼ばれる石油を生産することができる。
堆積物中の有機物(ケロジェン)は、熱分解、水素化、熱溶解などの高温処理を施さないとシェールオイルにならない。
そのため、合成原油と呼ばれる。
鉱物組成は産地により異なり、一般に粘土鉱物、ドロマイト、方解石、炭酸塩などを含む。
商業的に重要なオイルシェール層は、米国北西部のワイオミング州、ユタ州、コロラド州に分布している。
このシェールオイルは「タイトオイル」とも呼ばれ、石油の原油と同じようにそのまま、あるいは精製して使用することができる。
しかし、揮発性化合物の割合が多く、硫黄分が少ないのが特徴です。
熱処理によってオイルを製造すると、プロパン、ブタンなどの揮発性ガスや、ペンタン、天然ガソリン、ナフサなどの低沸点液体が多量に発生する。
低沸点成分の存在により、シェールオイルは極めて爆発性が高く、可燃性が高い。
原油とシェールオイルの違い
発生状況
原油は地下で高い圧力と温度で発生する。
この温度と圧力は貯留層の深さによって変化する。
シェールオイルは、閉じ込められた炭化水素を原油に変えるのに十分な圧力と温度にさらされていない。
シェールオイルに含まれるケロジェンは、自然のプロセスによって穏やかに原油に変換される。
原油とシェールオイルの化学組成
| 元素|原油中の割合|シェールオイル中の割合 | ||
| 炭素|83-85|-|水素|10-14 | ||
| 水素 10- 14 | ||
| 窒素|0.1~2|1.5~2|0.05~1.5 | ||
| 酸素|0.05〜1.5|0.5〜1 | ||
| 硫黄|0.05- 6.0|0.15-1 | ||
| 金属 |
表2. 代表的な原油とシェールオイルの化学組成(重量比
統計的評価によれば、代表的なシェールオイルは在来型原油と比較して、窒素化合物が多く、酸素化合物が多く、硫黄分が少ないことがわかる。
シェールオイルは酸素含有量が多いため、フリーラジカルが生成されやすく、燃料の燃焼が促進される。
原油とシェールオイルの性質
在来型原油は、天然には液状で貯留されている。
流動性が高く、-60〜30℃の高温域で注ぐことができる。
シェールオイルは、石油頁岩中の固体ケロジェンの熱分解により生成される合成原油です。
原油よりも流動性が低く、24~27℃の温度で注ぐことができる。
原油とシェールオイルの利用状況
原油を分留することで、ガソリン、ジェット燃料、軽油、灯油など多くの輸送用燃料が生産される。
また、プラスチック、医薬品、肥料、農薬、溶剤など、多くの化学製品の原料として使用することができます。
Shale oil is mainly used as heating oil, marine fuel or chemical for railroad wood preservative, etc. Unlike crude oil, this is not frequently used as a raw material for chemical products. However, high boiling point compounds in shale oil can be used to produce middle distillates such as kerosene, diesel, jet fuel, etc. Additional thermal cracking require producing low boiling point gasoline. Transportation fuels produced by shale oil is of low quality compared to higher grade conventional fuels.
Speight, J., Synthetic fuels handbook: properties, process, and performance. 2008
Speight, J. G., The chemistry and technology of petroleum(スピイト,J.G.石油の化学と技術). CRC press: 2014.
オラー,G. A.; モルナー,A., 炭化水素化学. John Wiley & Sons: 2003.
“Crude Oil Distillation-fr.svg” Image originale: Psarianos, Theresa knott; image vectorielle: Rogilbert derivative work: (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
「オイルシェール” By Georgialh – 自作, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
保存する
