
主な違い – イオン結合 vs 共有結合 vs 金属結合
結合は、一次結合と二次結合の2つに大別される。
一次結合は分子内の原子を結合する化学結合であり、二次結合は分子同士を結合する力です。
一次結合には、イオン結合、共有結合、金属結合の3種類があります。
二次結合には、分散結合、双極子結合、水素結合があります。
一次結合は二次力と比較すると結合エネルギーが比較的高く、安定です。
イオン結合と共有結合、金属結合の主な違いはその形成にある。
イオン結合はある原子が別の原子に電子を提供することで形成されるが、共有結合は2つの原子が価電子を共有することで形成され、金属結合は金属格子内で可変数の原子が可変数の電子を共有することで形成される。
今回は、その考察を行う。
-
イオン結合とは何か?
– 定義、形成、性質 -
共有結合とは何か?
– 定義、生成、性質 -
金属結合とは?
– 定義、形成、性質
イオン結合とは
Certain atoms tend to donate or receive electrons in order to become more stable by completely occupying their outermost orbit. Atoms with very few electrons in their outermost shell tend to donate the electrons and become positively charged ions, while atoms with more electrons in their outermost orbit have a tendency to receive electrons and become positively charged ions. When these ions are brought together, the attraction forces are occurred due to opposite charges of ions. These forces are called ionic bonds. These stable bonds are also called electrostatic bonds. Solids bonded with ionic bonds have crystalline structures and low electrical conductivity, which is due to lack of free moving electrons. Bonds usually occur between metal and non-metal that are having a large difference in electronegativity. Examples of ionically bonded materials include LiF, NaCl, BeO, CaF2 etc.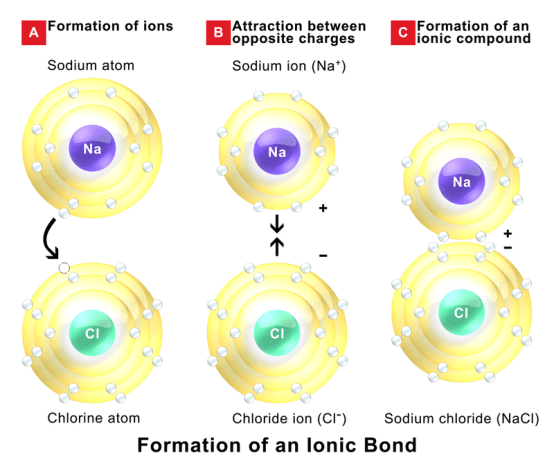
共有結合とは?
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share their valence electrons. The two atoms have a small difference in electronegativity. Covalent bonds occur between same atoms or different types of atoms. For example, fluorine needs one electron to complete its outer shell, thus, one electron is shared by another fluorine atom by making a covalent bond resulting F2 molecule. Covalently bonded materials are found in all three states; i.e., solid, liquid and gas. Examples of covalently bonded material include hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, water molecules, diamond, silica etc. 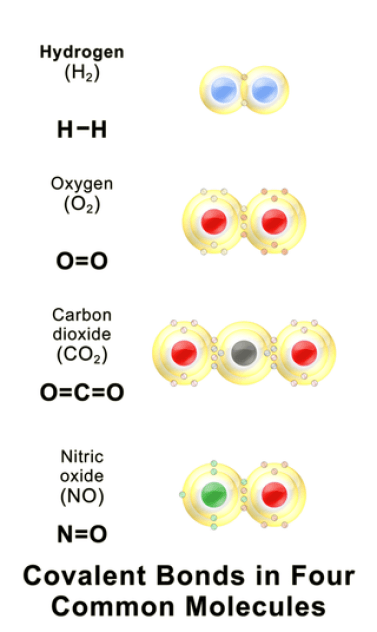
金属間化合物とは
In a metal lattice, valence electrons are loosely attached by the nuclei of metal atoms. Thus, valence electrons require very low energy to release themselves from nuclei. Once these electrons detach, metal atoms become positively charged ions. These positively charged ions are surrounded by a large number of negatively charged, free moving electrons called an electron cloud. Electrostatic forces are formed due to the attractions between the electron cloud and ions. These forces are called metallic bonds. In metallic bonds, almost every atom in the metal lattice shares electrons; so there is no way to determine which atom shares which electron. Because of this reason, electrons in metallic bonds are referred to as delocalized electrons. Due to the free moving electrons, metals are known for good electricity conductors. Examples of metals with metallic bonds include iron, copper, gold, silver, nickel etc.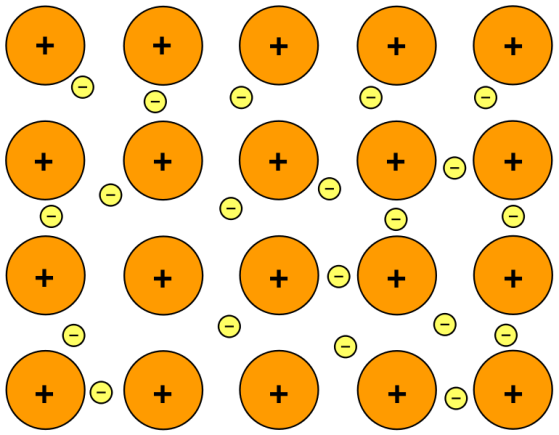
イオン性共有結合と金属性結合の違い
定義
イオン結合: マイナスイオンとプラスイオンの間に生じる静電気力。
共有結合。
共有結合は、2つの元素が価電子を共有し、中性気体の電子配置を得るために生じる結合です。
金属結合。
金属結合は、負に帯電した自由に動く電子と正に帯電した金属イオンの間の力です。
ボンドエナジー
イオン結合。
金属結合より結合エネルギーが高い。
共有結合。
金属結合より結合エネルギーが高い。
金属結合。
結合エネルギーが他の主結合より低い。
フォーメーション
イオン結合。
イオン結合は、ある原子が別の原子に電子を提供することによって形成される。
共有結合。
共有結合は、2つの原子が価電子を共有することによって形成される。
金属結合。
金属結合は、金属格子の中で、可変数の原子が可変数の電子を共有することによって形成される。
導電率
イオン結合。
イオン結合は導電率が低い。
共有結合。
共有結合の導電率は非常に低い。
金属結合。
金属結合は電気や熱の伝導性が非常に高い。
融点・沸点
イオン結合。
イオン結合は融点・沸点が高い。
共有結合。
共有結合は融点、沸点が低い。
金属結合。
金属結合は融点、沸点が高い。
物理的状態
イオン結合。
イオン結合は固体の状態でのみ存在する。
共有結合。
共有結合は、固体、液体、気体の形で存在する。
金属結合。
金属結合は固体の形でしか存在しない。
債券の性質
イオン結合。
結合は無指向性です。
共有結合。
結合の方向性があります。
金属結合。
結合の方向性がない。
硬度
イオン結合。
イオン結合は結晶構造のため、硬い。
共有結合。
共有結合は、ダイヤモンド、シリコン、カーボンを除いてあまり硬くはない。
金属結合。
金属結合はあまり硬くない。
可鍛性
イオン結合。
イオン結合を持つ材料は、可鍛性はない。
共有結合。
共有結合を持つ材料は可塑性がない。
金属結合。
金属結合を持つ材料は可鍛性です。
延性
イオン結合。
イオン結合を持つ材料は延性がない。
共有結合。
共有結合を持つ材料は延性がない。
金属結合。
金属結合を持つ材料は延性があります。
例
イオン結合。
LiF, NaCl, BeO, CaF2 など。
共有結合。
水素ガス、窒素ガス、水の分子、ダイヤモンド、シリカなど。
金属結合。
例:鉄、金、ニッケル、銅、銀、鉛など。
Cracolice, Mark. 入門化学の基礎と数学の復習. 2nd ed. N.p.: Cengage Learning, 2009. プリント
Duke, Catherine Venessa. A., and Craig Denver Williams. 環境と地球科学のための化学. N.p: CRC Press, 2007. 印刷する。
Garg, S. K. Comprehensive Workshop Technology. N.p: N.p.: Laxmi Publications, 2009. プリント
画像提供
「イオン結合” By BruceBlaus – 自作 (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
「共有結合” By BruceBlaus – 自作(CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
“金属結合” By Muskid – 自作 (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia

