主な相違点 – アリル vs ビニル
アリルとビニルは2つの異なる有機官能基です。
どちらもC-C二重結合を持ちますが、位置が異なります。
ビニル基では、C=Cは鎖の残りの部分に直接結合しています。
これに対し、アリル基は-CH2基を介して分子の残りの部分に結合しています。
これがアリル基とビニル基の主な違いです。
Vinylとは
Vinyl indicates the –CH=CH2 functional group, which can be formed by removing hydrogen from ethylene molecule. Therefore, the general molecular formula of vinyl compounds is R- CH=CH2, where R is any other group of atoms. Vinylic groups have sp2 hybridized carbon atoms. These compounds are very reactive, and readily polymerize to form vinyl polymers. Polyvinyl chloride, polyvinyl fluoride, and polyvinyl acetate are some examples of vinyl polymers. The Figure 1. Illustrates the mechanism of polyvinyl chloride synthesis.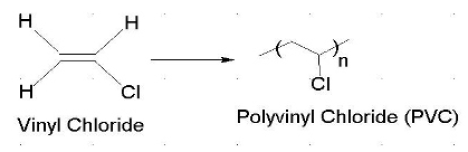
図1. フリーラジカルによるビニル重合機構
ビニル化合物は、耐久性があり、安価であることなどから、一般にプラスチック製造に使用されている。
また、ビニルは様々な添加剤や改質剤と組み合わせることができるため、他にも多くの用途があります。
アリルとは
Allyl indicates a functional group with structural formula H2C=CH-CH2-R, where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of methylene bridge (-CH2-) in between the vinyl group (-CH=CH2) and the rest of the molecule. Therefore, allyl group contains sp2 hybridized vinyl carbon atoms and sp3 hybridized allyl carbon atom. The allylic carbon atom is more reactive than normal alkanes, and it can easily form a stable carbocation because it is adjacent to vinyl carbon that can delocalize electrons to stabilize the positive charge. The Figure 2. Illustrates the resonance stabilization of allylic carbocation.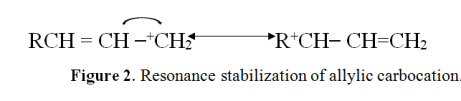
アリル化合物はカルボカチオンが安定なため、反応中に放射状に中間体を形成する。
例えば、SN1反応。
アリルとビニルの違い
一般分子式
アリルです。
一般的な分子式はRCH2CH=CH2です。
ビニル基は-CH2-基を介して他の分子と結合している。
ビニル基。
一般的な分子式はRCH=CH2。
ビニル基は分子内に直接結合している。
炭素骨格のハイブリッド化
アリル。
sp2混成の炭素原子に隣接してsp3混成のアリル炭素原子を含む。
ビニル。
sp2混成の炭素原子を含む。
用途
アリル アリル化合物は、天然ゴムやテルペン類の生合成など、多くの天然物の前駆体です。
ビニル ビニル化合物は、PVC、PVF、PVAcなどのビニル系ポリマーを製造することができる。
カルボカチオンの安定性
アリル アリル:電子の非局在化により安定なカルボカチオンを形成することができる。
Vinyl: Vinylic carbocations are very unstable due to lack of p-character.
